Top Solar Friendly States Lead US in CO2 Cuts

The US made CO2 cuts of 10% in the first thirteen years of the 21st century, per the EIA, primarily thanks to the solar friendly states.
The US Energy Information Agency (EIA) has released a report looking at carbon emissions by state. Just counting from 2000 till 2013, 37 states have reduced their emissions and 13 other states raised them in that time. Tallied together, the US has cut its total CO2 emissions by 9.6%.
As of 2013, the solar-friendly states now have the lowest CO2 emissions per capita.
California and the “RGGI states” in the northeast that embraced renewables wind and solar have the lowest CO2 emissions per capita, at around 9 metric tons per person – like Europe.
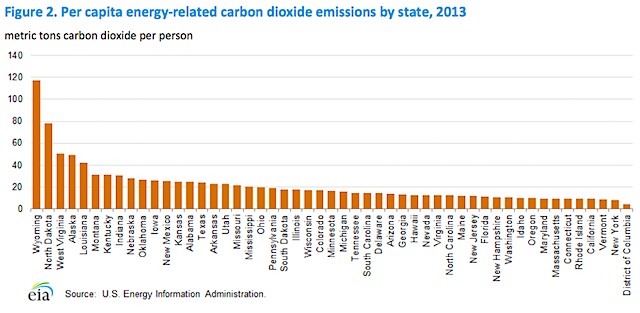
The Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) states – that deliberately cut CO2 by switching from fossil energy since 2006, now have the lowest CO2 emissions per capita by 2013 – Connecticut, Delaware, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, New York, Rhode Island and Vermont.
Of these; New York had the absolute lowest CO2 emissions per capita — 8 metric tons per capita. New York also made the greatest absolute CO2 cut at 52 million metric tons of CO2, for a 25% reduction.
The lowest per capita CO2 states are decisively those with more renewables, and of these, New York is the clear winner.
Not only does the New York have more renewable energy like solar, but the fact that almost half the 20 million people in the state live in NYC where they get around by subway, and are packed into multi-story townhouses with efficient heating and cooling, and have low energy-consuming jobs.
The RGGI states and California emitted only 8 or 9 metric tons of CO2 per capita, while Wyoming emitted the most: 117 metric tons per person.
Wyoming emitted 117 tons per capita, North Dakota emitted 78 metric tons; West Virginia, 50; Alaska 49, and Louisiana, 42, for the top five states in per capita CO2 emissions.
The EIA tallies each state’s emissions – not in the state where the coal or oil is dug out of the ground – but in the state where that fuel is burned.
For coal or natural gas, this would be the state that burns the fuel in its power plants, even if it then sends that electricity to be used in another state.
But for oil and gas, this means that – apart from what it uses to supply its own energy extraction needs – the state that ships oil or gas out of state is not the one that tallies the emissions.
Instead, the CO2 emissions from that coal extracted in Wyoming, or oil extracted in Alaska or Louisiana gets counted in the state where the fuel is burnt in the millions of cars and trucks on the roads throughout the nation.
Larger population, larger emissions.
The two most populous states have higher absolute emissions, of course. So Texas with nearly 30 million and California with nearly 40 million people obviously have higher absolute numbers for CO2 emissions. The dozen or so states with fewer than a million people, obviously have lower absolute emissions.
But the good news is that every state is more states are joining the clean energy revolution and cutting down emissions.
Image Credit: EIA and FlickR under CC license.
